- Home›
- Medical Devices›
- Injection Instruments›
- Injection & Precision Instruments›
- Disposable Syringes
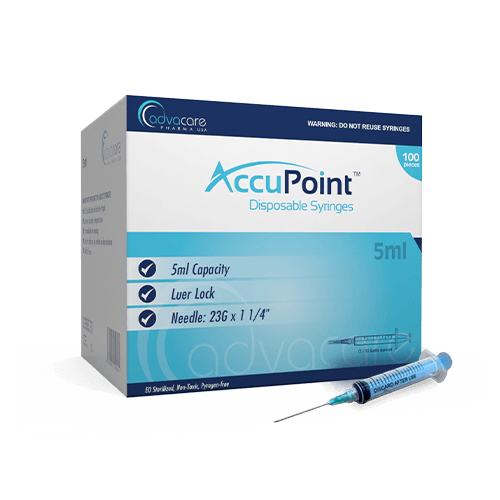
Disposable Syringes
Part
Tip
Tip Type
Needle
Capacity
Packaging
What are Disposable Syringes?
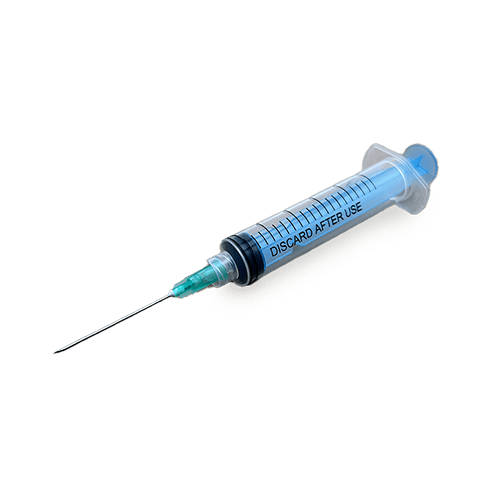
Disposable Syringes are designed for one-time use to inject medications or withdraw fluids from the body. Single-use syringes are made from high-quality medical grade materials and are available in various sizes ranging from 1ml to 60ml, depending on the volume of medication or fluid to be given or taken.
Disposable syringes are available in different types, including Luer Lock and Luer Slip, with the former being preferred due to their secure attachment to needles to prevent accidental disconnection. The markings on the barrel ensure accurate measurement and administration.
In addition to their use in medical settings, disposable syringes are also used in various industries, including research and development, veterinary medicine, and agriculture. The convenience and safety of single-use syringes make them a popular choice for a variety of applications.
Our Disposable Syringes are manufactured in facilities in China, India, and the USA, and undergo rigorous quality control procedures to ensure that they meets the highest standards of safety and performance. AdvaCare Pharma's commitment to excellence is evident in every aspect of our production process.
Product Specifications
Part
Tip
Tip Type
3-Part
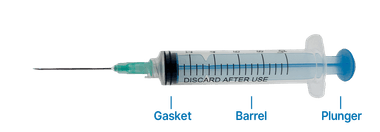
3-part disposable syringe is composed of three essential components: the barrel, plunger, and gasket. The gasket is usually made of synthetic rubber to ensure maximum accuracy and prevent any leakage of the drug or injectable substance. The 3-part syringe design is widely used due to its durability, accuracy, and easy-to-use features.
2-Part
2-Part disposable syringe is composed of a barrel and plunger only, with no gasket. This type of syringe is typically less expensive than 3-part syringes and is often used in low-risk applications, such as administering oral medications. The absence of a gasket in 2-part syringes means there is a slightly higher risk of fluid leakage during injection, but this risk can be minimized by ensuring the plunger is pushed in smoothly and evenly.

Luer Lock Tip
Luer Lock Tip disposable syringes feature a threaded tip that allows needles to be screwed on and securely locked in place. This design minimizes the risk of accidental disconnection between the needle and the syringe, ensuring that no liquids leak out during administration. The Luer Lock tip is commonly used in medical settings where precise and controlled medication delivery is necessary.

Luer Slip Tip
Luer Slip Tip disposable syringe allows a needle to be easily and quickly pushed straight onto the end of the tip for convenient use. This type is widely used in medical settings for administering medications and withdrawing fluids from the body. The Luer Slip tip is designed to provide a secure connection between the syringe and the needle, while also allowing for quick and easy attachment and removal.
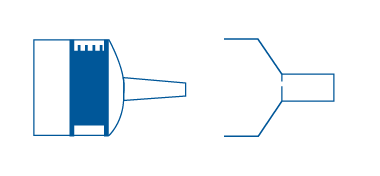
Centric Tip
Centric Tip disposable syringe is designed with the tip positioned at the center of the bottom end. This type of tip is commonly used for standard injections where the needle needs to be inserted at a perpendicular angle to the skin or other surface. The centric tip provides accurate placement of the needle and prevents the needle from wobbling or moving during the injection.
Eccentric Tip
Eccentric Tip disposable syringe has a tip that is slightly off-center and aligned with the outer body of the barrel, allowing for better access and visibility during injections or aspirations. This type of syringe is commonly used in medical procedures where precise placement is required. The eccentric tip can help to reduce the risk of tissue damage or discomfort to the patient.
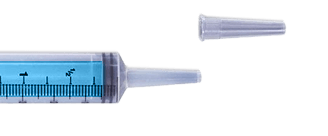
Catheter Tip
Catheter Tip disposable syringes have a longer, tapered tip that is designed to allow for easy insertion into catheters or other medical devices. The slip tip design allows for smooth and easy delivery of fluids or medications, making them ideal for use in hospitals, clinics, and other medical settings. The catheter tip is commonly used for procedures that require the injection or withdrawal of fluids from hard-to-reach areas.
Why are we a top Disposable Syringes manufacturer?
AdvaCare Pharma is a leading Disposable Syringes manufacturer with CE and ISO-certified facilities that adhere to strict quality control guidelines. The AccuPoint™ brand is known for its superior performance and innovative solutions that have been trusted by healthcare professionals around the world.
As a globally-focused manufacturer of disposable syringes, we understand the unique challenges faced by medical distributors in the healthcare industry, and we are dedicated to providing the highest level of customer service and support. Our teams of sales, regulatory and product specialists are available to offer guidance and answer any questions, and we are committed to ensuring that our medical devices reach our distributors in a timely and efficient manner.
Uses
How should Disposable Syringes be utilized?
Disposable Syringes are indispensable for the single-use injection or precision extraction of fluids, following rigorous safety and efficacy guidelines.
Prior to application, examine the syringe's calibration to guarantee accurate dosage. Checking that the syringe remains uncontaminated and that the needle is firmly affixed is paramount for a successful procedure.
Healthcare providers must adhere to proven protocols to confirm substances are administered or withdrawn safely and accurately.
How should Disposable Syringes be disposed of?
The disposal process for disposable syringes is all-important in mitigating risk factors. Following their application, these syringes must be treated as medical waste, abiding by the protocols set for the management of healthcare waste. For the sake of safety and to lessen the chance of unintended injuries from needles, it is advisable to immediately place used syringes into allocated sharps disposal units. These units are designed to securely contain sharp objects, helping to maintain safety standards in medical settings.
What precautions should be observed before using Disposable Syringes?
Prior to the employment of Disposable Syringes, several preparatory measures should be carefully considered to maintain procedural security and efficiency. An initial evaluation of the syringe’s packaging is required to identify any signs of compromise which could suggest sterility issues or pose safety hazards.
Healthcare practitioners must also verify the syringe's expiry date so it is suitable for use, as expired syringes risk diminished sterility and, consequently, treatment integrity. The use of a pristine, sealed syringe for every procedure is imperative to avert contamination risks, underlining the importance of these syringes in achieving successful medical outcomes.
FAQs
How does a Disposable Syringe work?
A disposable syringe is designed for single-use to administer medication or withdraw fluids from the body. The plunger is inserted into the barrel and pulled back or pushed forward to draw or dispense the medication or fluid.
What is the difference between 3-part and 2-part Disposable Syringes?
3-part disposable syringes consist of three separate pieces: barrel, plunger, and rubber piston, while 2-part syringes have only two pieces: barrel and plunger. 2-part syringes are generally more cost-effective and are easier to handle and assemble.
What is the difference between luer lock and luer slip tips?
Luer lock tips have a threaded connection that screws onto the needle hub for a secure and leak-proof fit. Luer slip tips simply slide onto the needle hub and require extra care to avoid accidental disconnection.
What are the different tip types of Disposable Syringes?
Centric tips are designed for general-purpose use, eccentric tips are for specialized injection procedures such as intradermal injections, and catheter tips are used for the administration of fluids through a catheter.
How should Disposable Syringes be stored and handled?
Disposable syringes should be stored in a clean, dry, and cool place away from direct sunlight and sources of heat or humidity. They should be handled with clean hands and properly disposed of in a sharps container after use to avoid contamination and injury.
Can I request samples of your Disposable Syringes for evaluation?
Yes, we provide samples of our medical devices for evaluation and product registration. Get in touch with our International Sales Department to request samples and discuss your unique needs.
Do your Disposable Syringes bear the CE mark?
Our medical devices are certified with the CE mark, signifying compliance with European Union regulations. Moreover, our manufacturing procedures adhere rigorously to ISO standards for consistent quality and safety assurance.
Do you offer regulatory support for importing your Disposable Syringes?
We offer extensive regulatory support to our distributors, aiding in navigating local regulations and facilitating the importation of our medical devices. With the expertise of our Regulatory Affairs Department, which includes qualified professionals such as pharmacists, biomedical engineers, QA specialists, and documentation experts, we ensure a seamless product registration experience.
How can I obtain pricing information for your Disposable Syringes?
Pricing information for our medical devices is available upon request. Please contact our International Sales Department to receive a quotation and discuss distribution opportunities.
Do you offer marketing support for distributors of your Disposable Syringes?
Yes, we provide extensive marketing support and resources, including but not limited to printed materials, merchandising and digital activations, to help distributors promote our medical devices, build brand awareness and effectively distribute our products in their respective markets.
What other types of medical devices does your company manufacture?
AdvaCare Pharma specializes in manufacturing a broad spectrum of more than 500 Class I and Class II medical devices, including surgical instruments, diagnostic devices, medical disposables, wound care products, and urological devices.
References
Reuse of disposable syringes and needles in patients with type 2 diabetes
This study on the reuse of disposable syringes among patients with type 2 diabetes offers a critical examination of a common but risky practice in diabetes management. It sheds light on the frequency and underlying reasons why individuals with type 2 diabetes might reuse syringes and needles intended for single use, a practice that significantly increases health risks such as infections and the transmission of bloodborne pathogens. The research underscores the gap in patient education regarding the safe use of syringes and the crucial role healthcare providers play in advocating for single-use practices to safeguard patient health.
This study highlights the need for comprehensive educational programs that not only focus on the proper use of diabetes management tools but also emphasize the health implications of reusing medical disposables. By understanding the socioeconomic and informational barriers that lead to this practice, the study calls for targeted interventions to promote safer injection practices among diabetes patients, aiming to reduce the incidence of needle-stick injuries and the spread of infections. This in-depth analysis contributes significantly to the ongoing discussions on improving diabetes care and patient safety.

You might be interested in...
Why AdvaCare Pharma?
As an industry leader, we are aware of our responsibility to provide affordable and sustainable solutions to improve healthcare worldwide.